Fish gill whole cell biosensing on chip
The objective of the present work package is the development of a fish gill cell microfluidic biosensor platform. To achieve this, we aim to transfer the technology developed for human lung epithelia to fish gill cell epithelial growth and transepithelial resistance (TER) measurements, and to test the biosensor for exposure to metals in the laboratory and field, measuring the TER response and using intracellular biomarkers of exposure. The initial phase of proof-of-concept for the detection of response to cadmium and benzo(a)pyrene is presented here.
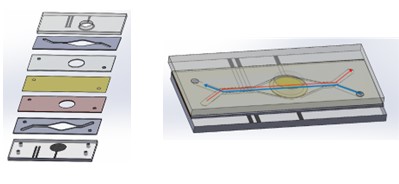
Biochip Design v4.0
We are currently using microfluidic Biochip Design v4.0, which incorporates a PET membrane separating the top (apical) and bottom (basolateral) chambers (Figure 1). After several trials, a Y-shaped channel design has proven best for maintaining constant pressure. This setup allows test media to be applied to the apical chamber and media, mimicking blood flow to the basolateral chamber. The flows are counter-current, mimicking the water and blood flow of a fish gill. The next phase of the project will involve incorporating electrodes for TER measurements.
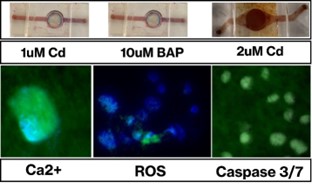
Intracellular biomarkers of exposure
We have cultured the rainbow trout rtGill cell line on membranes within Biochip Design v3.0 and v4.0 and exposed cells to apical and basolateral flows with cadmium or benzo(a)pyrene. Fluorescent biomarkers for perturbed calcium homeostasis, reactive oxygen species generation and apoptosis where visualised via fluorescent microscopy (Figure 2). The next phase will introduce TER measurements, exposure to natural waters, and trials with primary gill cell cultures.
Author: Dr. Nic Bury
Keywords
Gill cell culture, biomarkers, effect-based monitoring, cadmium, BaP, reactive oxygen species, intracellular calcium, apoptosis





